Introduction
Newborn stem cell banking preservation, also known as cord blood banking or cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSCs) banking, has emerged as a significant decision for many parents, driven by the potential benefits it offers for the future health and well-being of their child. The remarkable ability of stem cells collected from a newborn’s umbilical cord blood and tissue to differentiate into various cell types makes them valuable for medical treatments and ongoing research. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the factors influencing the cost of newborn stem cell banking preservation, explore the potential medical applications of preserved stem cells, and provide insights into the clinical implications of this cutting-edge technology.

Factors Affecting the Cost of Stem Cell Banking Preservation
To make an informed decision about newborn stem cell banking preservation, it is essential to understand the factors that influence its cost. The cost of stem cell banking preservation can vary based on several key factors:
- Type of Stem Cell Banking Banking Preservation
Stem cell preservation can involve different types, such as cord blood stem cell banking and cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSCs) banking. The type of preservation chosen can impact the overall cost, considering the harvesting process and procedures involved.
- Private vs. Public Preservation
Parents can opt for private preservation to exclusively store their child’s stem cells for personal use by the child or their family. Alternatively, they may choose public preservation, where the stem cells are donated for potential use by others. Private preservation generally incurs higher costs due to the need for long-term storage and maintenance of stem cells banking.
- Collection and Processing Fees
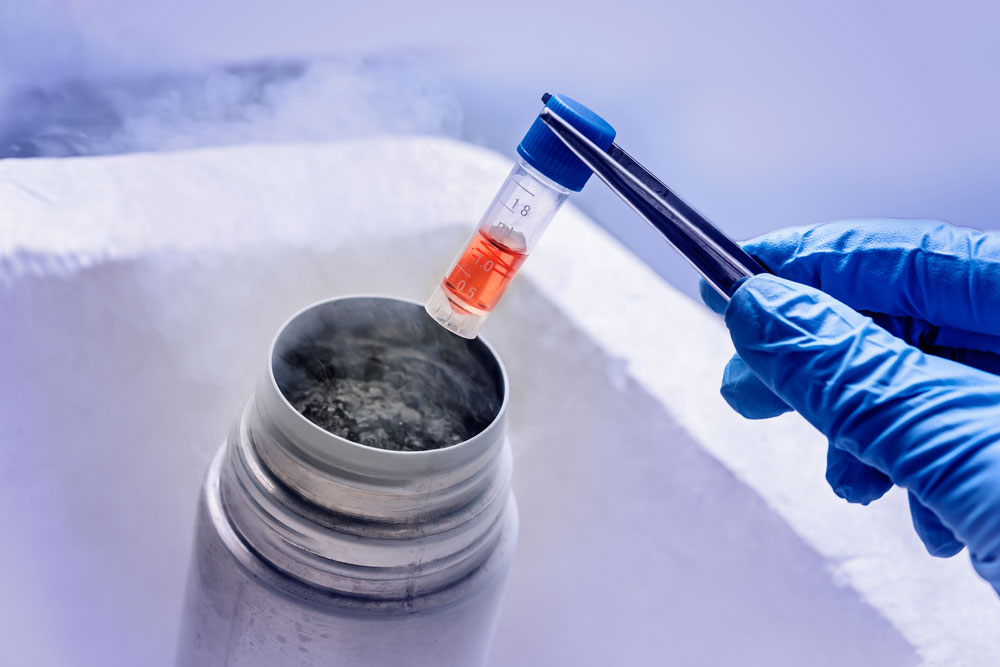
The process of harvesting and cryopreserving the stem cells requires specialized equipment, expertise, and laboratory procedures. These costs are typically included in the overall preservation fees. The collection process begins with obtaining the umbilical cord from the hospital immediately after delivery, followed by transporting the cord blood and tissue to a specialized laboratory for processing and cryopreservation.
- Storage and Maintenance Fees
Storing and maintaining the preserved stem cells over time incurs ongoing costs. The stem cells must be stored in specialized facilities equipped with advanced cryopreservation techniques to ensure their viability and longevity. The quality, security measures, and accreditation of the storage facility may influence the cost.
- Additional Services or Add-Ons
Some stem cell preservation providers may offer additional services or add-ons that can impact the overall cost. These may include expanded genetic testing, genetic counselling, or the ability to store additional samples from the umbilical cord tissue. Parents should consider these optional services in relation to their budget and preferences.
- Financing and Payment Options
To make newborn stem cell banking preservation more accessible, many preservation facilities provide financing and payment options. These options may include monthly payment plans or discounts for upfront payments. Parents should inquire about these options and choose the one that aligns with their financial circumstances.
Newborn Stem Cell Banking Preservation Range of Costs
While the cost of newborn stem cell banking preservation can vary significantly based on the factors mentioned above, it is important to consider the long-term benefits and potential medical applications when evaluating the cost. On average, private preservation can range from several thousand dollars for initial collection and processing, along with annual storage fees. Public preservation, which involves donation, is typically free of charge for the donor.
The potential benefits of preserved stem cells, such as the treatment of blood-related disorders, regenerative medicine applications, and future medical advancements, must be weighed against the cost to make a well-informed decision.
Potential Applications of Newborn Stem Cells
The clinical implications of newborn stem cell banking preservation are vast, and the potential applications of preserved stem cells continue to expand. Some of the key areas where these stem cells can be used include:
- Treatment of Blood-Related Disorders
Stem cells derived from newborn cord blood have demonstrated remarkable success in treating various blood-related disorders, such as leukemia, lymphoma, and anemia. These conditions often necessitate bone marrow or stem cell transplants, and cord blood can serve as a valuable source of compatible stem cells for transplantation.
- Regenerative Medicine
One of the most promising areas of application for newborn stem cells lies in regenerative medicine. The unique ability of stem cells to differentiate into various cell types makes them essential for repairing or replacing damaged or diseased cells and tissues. Stem cell therapies hold great promise in treating conditions like spinal cord injuries, heart disease, and neurological disorders.
- Future Medical Advancements
The preservation of newborn stem cell banking provides families with access to a valuable resource that may have future medical applications. Ongoing research and advancements in stem cell science may uncover new treatment modalities and expand the potential uses of preserved stem cells. By preserving their child’s stem cells, families can be prepared for future medical breakthroughs and personalized therapies.
- Compatibility and Reduced Rejection Risks
One of the significant advantages of using stem cells from a child’s cord blood is their compatibility with the child’s own tissues and organs. Additionally, these stem cells may also be compatible with immediate family members, reducing the risk of rejection or complications associated with finding a suitable donor from external sources, such as bone marrow registries.
- Ethical Considerations and Peace of Mind
Newborn stem cell banking preservation offers ethical considerations and peace of mind for families. It provides an alternative to discarding the umbilical cord, which would otherwise be considered medical waste. Knowing that they have taken steps to secure their child’s future health can bring a sense of reassurance and comfort to parents.
Conclusion
In conclusion, newborn stem cell banking preservation represents a pivotal decision for parents, offering potential life-saving benefits for the child and their family. The cost of preservation is influenced by factors such as the type of preservation, private vs. public options, collection and processing fees, storage and maintenance fees, additional services or add-ons, and available financing options. Despite the costs, the potential medical applications of preserved stem cells banking in treating blood-related disorders, advancing regenerative medicine, and contributing to future medical advancements make this a worthwhile consideration for many parents. Understanding the clinical implications of newborn stem cell preservation empowers parents to make informed choices that may positively impact the future health and well-being of their child.
For more information about CEXCI stem cell banking, please click on the button below to reserve your FREE consultation today!
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is newborn stem cell preservation?
Newborn stem cell preservation, also known as cord blood banking or cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSCs) banking, involves collecting and storing stem cells from a newborn’s umbilical cord blood and tissue. These stem cells have the remarkable ability to differentiate into various cell types, making them valuable for medical treatments and research.
What are the potential benefits of newborn stem cell preservation?
Newborn stem cells have shown immense potential in various medical applications, including the treatment of blood-related disorders, regenerative medicine, and future medical advancements. They offer compatibility with the child’s own tissues and reduce the risk of rejection in potential transplant situations.
What factors influence the cost of stem cell banking preservation?
The cost of newborn stem cell preservation is influenced by several factors, including the type of preservation (cord blood or cord MSCs), private vs. public preservation, collection and processing fees, storage and maintenance fees, additional services or add-ons, and available financing and payment options.
What are the different types of stem cell preservation?
There are two main types of stem cell preservation: cord blood stem cell banking and cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSCs) banking. Each type has its associated costs and potential medical applications.
What is the difference between private and public preservation?
Parents can opt for private preservation to exclusively store their child’s stem cells for personal use by the child or their family. Alternatively, they may choose public preservation, where the stem cells are donated for potential use by others. Private preservation generally incurs higher costs due to long-term storage and maintenance.
What are the collection and processing procedures for stem cell preservation?
The collection process starts with obtaining the umbilical cord from the hospital immediately after delivery. The cord blood is drawn using a sterile needle and stored in a special blood bag, while the cord tissue is collected and placed into a special collection kit. The collected samples are then transported to a specialized laboratory for processing and cryopreservation.
How much does newborn stem cell preservation cost?
The cost of newborn stem cell preservation can vary significantly based on the type of preservation, private or public option chosen, and any additional services or add-ons. On average, private preservation can range from several thousand dollars for initial collection and processing, along with annual storage fees. Public preservation, which involves donation, is typically free of charge for the donor.
What are the potential medical applications of newborn stem cells?
Stem cells derived from newborn cord blood and tissue have shown promising applications in the treatment of blood-related disorders, regenerative medicine, and future medical advancements. Ongoing research may uncover new treatment modalities and expand the potential uses of preserved stem cells.
How do parents decide whether to opt for newborn stem cell preservation?
Parents should carefully consider the long-term benefits and potential medical applications of preserved stem cells when evaluating the cost. Understanding the factors influencing the cost and exploring financing options can help parents make an informed decision that aligns with their goals and financial situation.
Is newborn stem cell preservation a worthwhile investment?
Newborn stem cell preservation represents a promising investment in the future of regenerative medicine and personalized healthcare. By preserving their child’s stem cells, families can secure a valuable resource that may hold the key to transformative medical therapies and potential personalized treatments in the future.